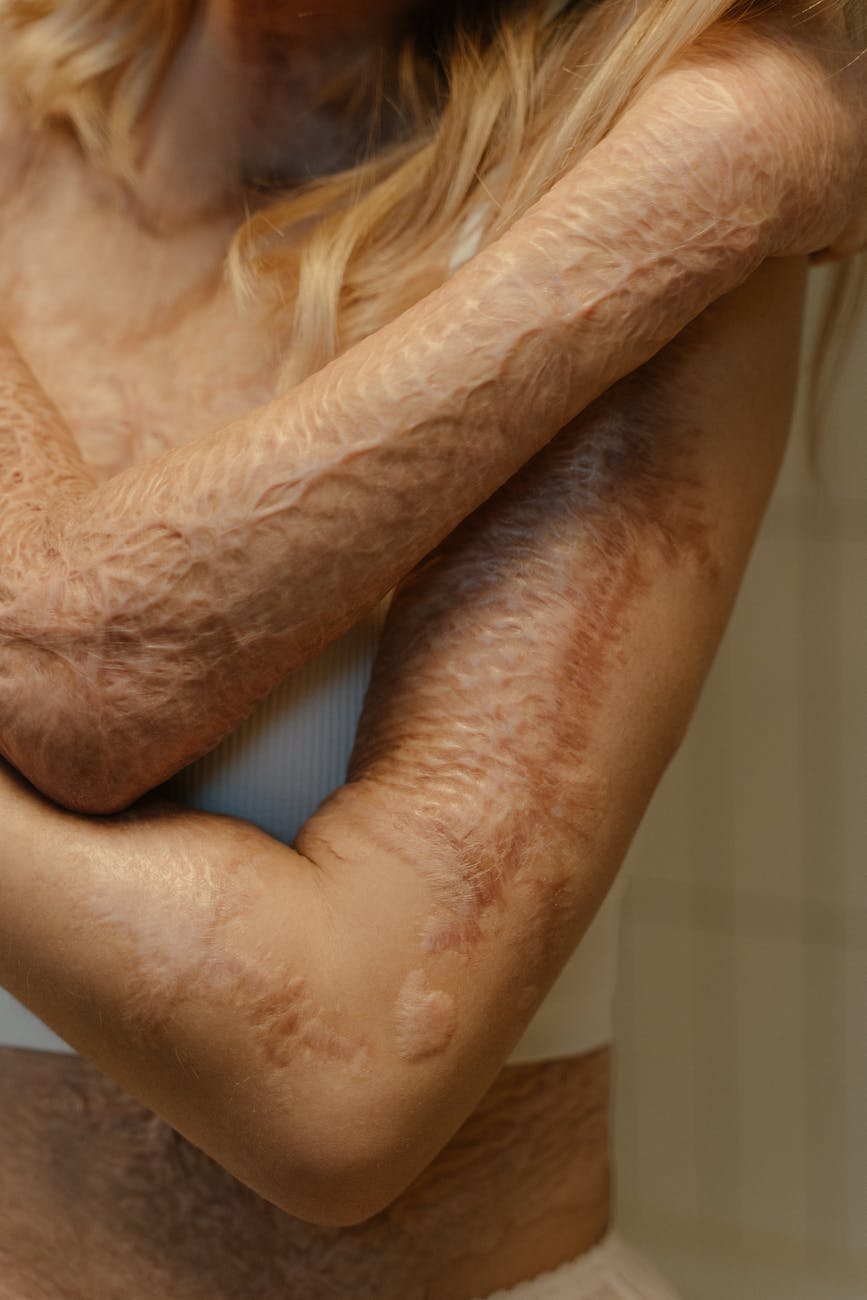
Different Kinds of Burns
Introduction
Different Kinds of Burns : Burns are a common injury that can happen to anyone at any time. Understanding the different types of burns, their causes, and how to provide immediate first aid is essential for everyone. In this article, we will explore various kinds of burns, their symptoms, treatment, and prevention measures.
Understanding the Types of Burns
First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns, also known as superficial burns, affect the top layer of the skin. They are usually caused by brief contact with hot objects, sunburn, or scalding from hot liquids. These burns are characterized by redness, pain, and minor swelling.
Second-Degree Burns
Second-degree burns, or partial-thickness burns, extend beyond the top layer of skin. They often result from exposure to hot liquids, flames, or chemicals. Blisters, severe pain, and redness are typical symptoms of these burns.
Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns, or full-thickness burns, are the most severe. They damage all skin layers, potentially affecting underlying tissues, muscles, and bones. These burns are often the result of prolonged exposure to flames, electricity, or chemicals. The skin may appear charred or white, and there might be no pain due to nerve damage.
Chemical Burns
Chemical burns occur when the skin comes into contact with corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, or solvents. The severity depends on the type of chemical involved and the duration of contact.
Electrical Burns
Electrical burns result from contact with electrical currents, causing damage to the skin and internal tissues. The severity depends on the voltage and the pathway the current takes through the body.
Radiation Burns
Radiation burns are a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. These burns can occur during medical treatments or nuclear accidents. Their severity depends on the duration and intensity of exposure.
Common Causes of Burns
Burns can result from various factors, including fire and flames, scalding, electrical accidents, chemical exposure, and radiation therapy. Each type of burn requires specific care and treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of burns may vary depending on their degree. Common signs include redness, pain, blisters, swelling, and, in severe cases, charred skin. It’s crucial to assess the burn’s severity to determine the appropriate course of action.
Immediate First Aid
In the event of a burn, immediate first aid is crucial. For first-degree burns, cool the affected area with cold water and apply a sterile dressing. For second-degree burns, avoid popping blisters and apply a clean, non-stick bandage. In the case of third-degree burns, cover the area with a sterile cloth and seek medical attention immediately.
Medical Treatment
Pain Management
Effective pain management is essential, especially for second and third-degree burns. Medical professionals may prescribe pain medication to alleviate discomfort.
Infection Control
Burn injuries make the skin vulnerable to infections. Preventing infection through proper wound care is crucial.
Skin Grafting
In severe cases, skin grafting may be required to replace damaged skin with healthy skin from another part of the body.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Burns can lead to complications such as infections, scarring, contractures, and even psychological trauma. Long-term effects can impact a person’s quality of life.
Preventing Burns
Prevention is key. Measures like using sunscreen, fire safety, electrical safety, and chemical handling precautions can help avoid burn injuries.
Burns in Children
Children are more susceptible to burns due to their curiosity and lack of awareness. Parents and caregivers must take extra precautions to protect children from burn injuries.
Psychological Impact
Dealing with burn injuries can be emotionally challenging. Understanding and addressing the psychological impact is essential for the overall well-being of burn survivors.
Conclusion
Burn injuries can be painful and life-altering. Knowing the types, causes, symptoms, and appropriate first aid and medical treatment is crucial. Additionally, taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of burns.
Six Directional Hazards and Precautions | Download PPT
10 Safety Rules of Construction Sites | Download PPT
How To Conduct Safety Induction for New Employees at Site | Download PPT
Safety Quiz for Safety Officer | Download PPT
Fire Safety | Fire Hazards and Precautions | Evacuation Plan | Download PPT
FAQs
- What should I do if I get a burn? If you get a burn, the first step is to cool the affected area under running cold water and then cover it with a clean, non-stick bandage. Seek medical help if the burn is severe.
- Are there any long-term effects of burns? Yes, burns can lead to scarring, contractures, and psychological trauma, which may have long-term effects on an individual.
- How can I prevent burn injuries at home? You can prevent burn injuries by practicing fire safety, electrical safety, and proper handling of hot objects or chemicals. Also, keep a close eye on children to avoid accidents.
- What is the most severe type of burn? Third-degree burns, also known as full-thickness burns, are the most severe. They affect all layers of the skin and may extend to underlying tissues.
- Can psychological support help burn survivors? Yes, psychological support is crucial for burn survivors to cope with the emotional and mental challenges that may arise from their injuries.
Knowledge is power.