Basic First Aid HSE Training
Slide 1: Basic First Aid – HSE Training
Basic First Aid – HSE Training
Presented by: HSE STUDY GUIDE
Date: 26/04/2025
Good morning team!
I hope you’re all doing great today.
Let’s talk about something that can literally save a life — Basic First Aid.
When an accident happens, what we do in the first few minutes can make all the difference. You don’t have to be a doctor — just knowing the basics can help stabilize a person and possibly prevent serious outcomes.
Let’s dive in and learn how to respond when seconds matter.
Slide 2: Objectives of the Training
By the end of this session, you’ll be able to:
- Understand the importance of first aid
- Respond to common injuries and emergencies
- Apply basic life-saving techniques
- Stay calm and act quickly in emergencies
- Know your role until professional help arrives
Slide 3: What is First Aid?
First aid is the immediate care given to an injured or ill person before medical professionals arrive.
Its goals are:
- Preserve life
- Prevent the condition from worsening
- Promote recovery
Even small actions can have big results in an emergency.
Slide 4: The 3 Ps of First Aid
The three main aims of first aid are often called the 3 Ps:
- Preserve Life – First and foremost
- Prevent Further Injury – Stop the situation from getting worse
- Promote Recovery – Help the person begin healing
Slide 5: First Aid Priorities – DRSABCD
Here’s a simple checklist to follow in emergencies:
D – Danger: Check for danger to yourself and the victim
R – Response: Check if the person is responsive
S – Send for help: Call emergency services immediately
A – Airway: Ensure the airway is clear
B – Breathing: Check if the person is breathing
C – CPR: Start chest compressions if not breathing
D – Defibrillation: Use AED if available
Remember: Your safety comes first.
Slide 6: Common Workplace Injuries
Some common situations where first aid may be needed:
- Cuts and bleeding
- Burns and scalds
- Sprains and fractures
- Electric shock
- Heat exhaustion or heatstroke
- Fainting or unconsciousness
Let’s look at how to handle each one safely.
Slide 7: Bleeding and Cuts
What to do:
- Apply pressure with a clean cloth
- Raise the injured part if possible
- Keep pressure until bleeding stops
- Apply a sterile dressing or bandage
- Seek medical attention for deep wounds
Never remove large objects stuck in wounds — leave that to professionals.
Slide 8: Burns and Scalds
For minor burns:
- Cool the area with running water for 10–20 minutes
- Do not apply ice, butter, or cream
- Cover with a clean, non-stick dressing
For serious burns:
- Do not remove burned clothing stuck to the skin
- Call emergency services
- Treat for shock if needed
Always take chemical or electrical burns seriously.
Slide 9: Fractures and Sprains
Signs of a fracture:
- Swelling, bruising, or obvious deformity
- Pain and inability to move the limb
What to do:
- Immobilize the area — don’t try to straighten it
- Apply a splint or support if trained
- Apply a cold pack to reduce swelling
- Call for medical help
Avoid moving the person unless necessary.
Slide 10: Heat-Related Illness
Heat exhaustion symptoms:
- Dizziness, sweating, nausea, muscle cramps
What to do:
- Move the person to a cooler area
- Give small sips of water
- Apply cool, damp cloths
- Monitor their condition
If they collapse or stop sweating — it may be heatstroke, a medical emergency.
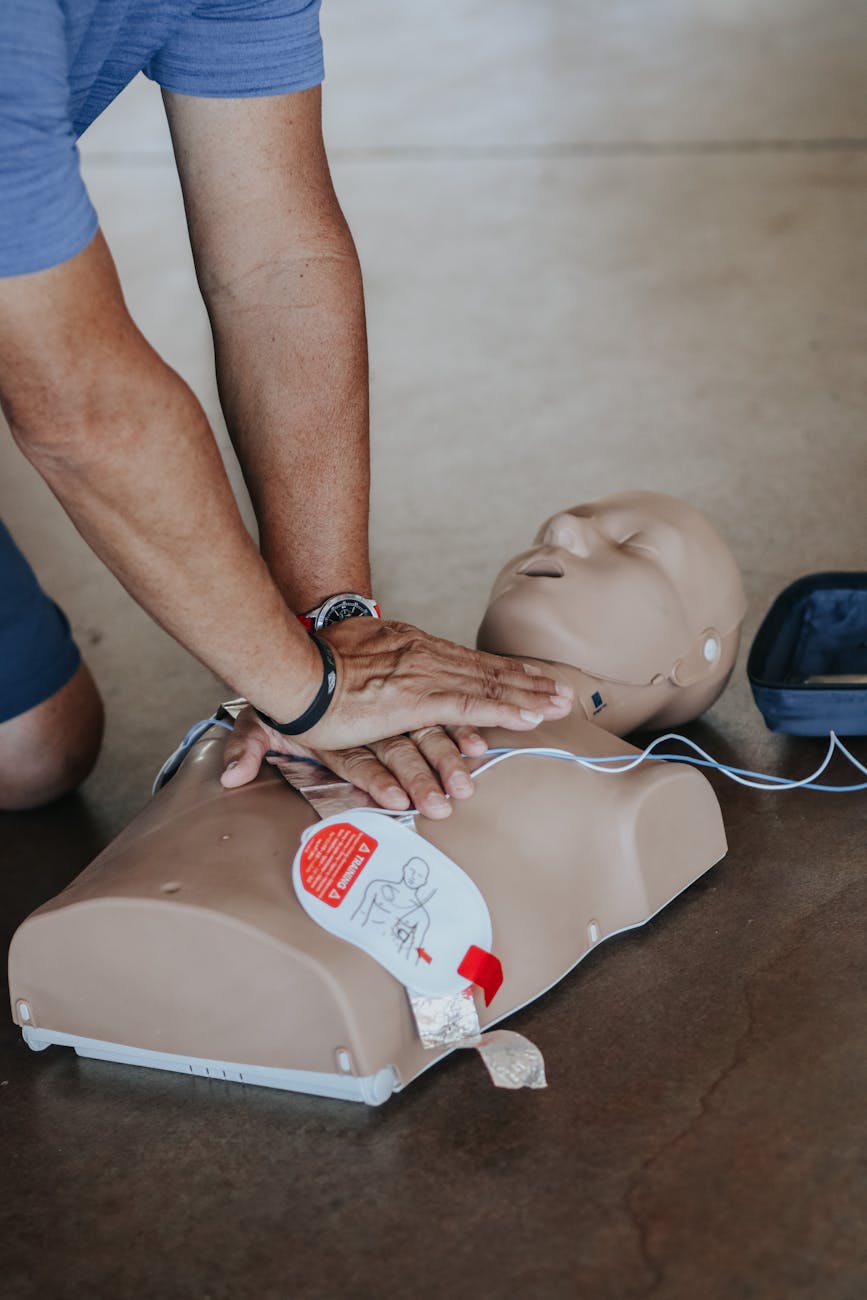
Slide 11: CPR – When and How
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is used when a person is unconscious and not breathing.
Steps:
- Place the heel of your hand on the center of the chest
- Interlock your fingers
- Push hard and fast — at least 100–120 compressions per minute
- If trained, give 2 rescue breaths after every 30 compressions
If unsure — just do compressions. It’s better than doing nothing.
Slide 12: AED – Automated External Defibrillator
An AED is a device used to restore normal heart rhythm.
How to use:
- Turn it on and follow voice prompts
- Attach the pads as shown in the diagram
- Make sure no one is touching the person during shock
- Continue CPR after the shock until help arrives
AEDs are designed for everyone to use — no medical degree needed.
Slide 13: Choking Response
If the person can’t speak, cough, or breathe:
- Perform the Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts)
- Stand behind the person, make a fist above their belly button
- Give quick upward thrusts until the object is expelled
If they become unconscious, begin CPR immediately.
Slide 14: First Aid Kit Essentials
Your workplace first aid kit should include:
- Sterile gauze and dressings
- Adhesive bandages
- Scissors and tweezers
- Antiseptic wipes
- Burn cream
- Gloves and CPR face shield
- Cold pack
- Emergency contact card
Check it regularly and report missing items.
Slide 15: Your Role in First Aid
- Stay calm and act quickly
- Always assess the situation first
- Know where the first aid kit and AED are located
- Report incidents immediately
- Get trained in first aid and CPR if you haven’t already
You might be the one to make the difference.
Slide 16: What NOT to Do
- Don’t panic — it won’t help anyone
- Don’t give food or drink to unconscious persons
- Don’t try to move someone with a suspected spinal injury
- Don’t use unclean materials for bleeding wounds
- Don’t wait to call for help — act fast
Slide 17: Real-Life Example
Scenario:
A worker collapsed from heatstroke during summer work. A teammate quickly moved him to shade, loosened his clothing, and applied cool towels while another called for help.
Outcome:
Paramedics confirmed that quick action likely prevented organ damage or worse.
First aid buys time until help arrives — and sometimes, that’s all it takes.
Slide 18: Questions and Discussion
Let’s open it up —
Have you ever had to give or witness first aid on site?
What challenges did you face?
Do you know where the nearest first aid kit is?
Let’s share and learn together.
Slide 19: Thank You
Thank you, team, for your time and attention today.
Basic First Aid isn’t just for the workplace — it’s a life skill that could help your family, friends, or a stranger someday.
Let’s stay alert, stay trained, and stay ready.
And don’t forget — follow HSE STUDY GUIDE for more safety updates!
Lockout and Tagout Procedure HSE Training